What is an off-grid solar power system?
An off-grid solar power system is a setup that generates and stores electricity independently of the traditional utility grid. It’s designed to operate autonomously, which makes it perfect for remote locations, cabins, or anyone who wants energy independence. It is designed to generate and store electricity for use in locations where there is no access to the grid or where grid connection is costly or unreliable.
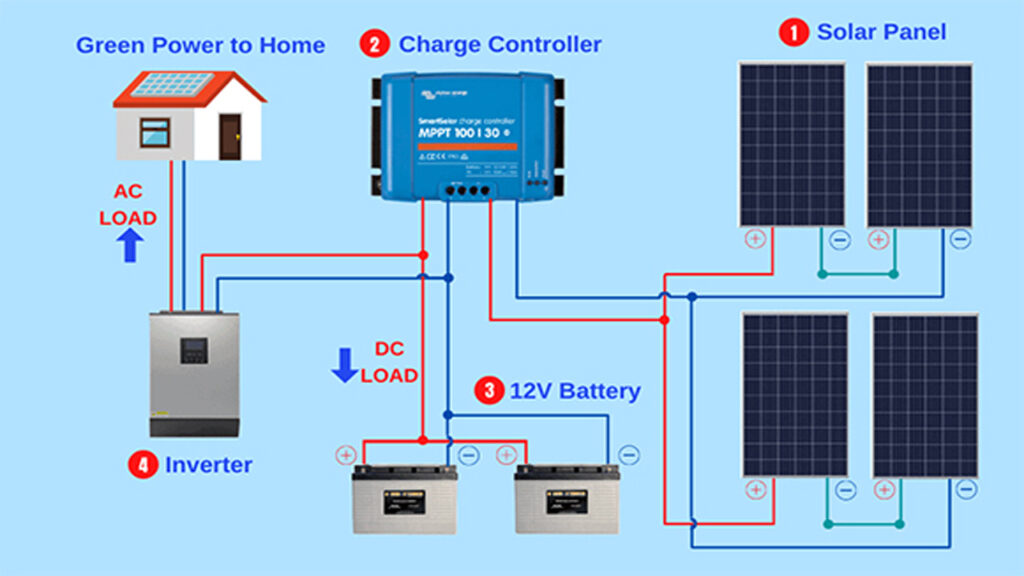
🔋 Main Components of an Off-Grid Solar System:
A typical solar system consists of solar panels (which absorb sunlight), an inverter (which converts DC into AC), mounting structure (that hold the panels in place), batteries (to store the extra power generated), a grid box and balance of systems (wires, nuts etc.). A solar system comes in various sizes like 1 kWh, 2 kWh 3kW, 5kW, 7.5 kW, and 10 kW.
- Solar Panels – These convert sunlight into electricity (DC – direct current).
- Charge Controller – Regulates the voltage and current from the solar panels to protect the batteries.
- Battery Bank – Stores the electricity for use when the sun isn’t shining (e.g. at night or during cloudy weather).
- Inverter – Converts stored DC electricity into AC (alternating current), which is what most household appliances use.
- Backup Generator (optional) – Provides power if solar generation is insufficient, especially during long cloudy periods.
How an off-grid solar power system works:
- Solar Panels: Solar panels, made of photovoltaic (PV) cells, capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The number and size of solar panels determine the amount of electricity generated.
- Charge Controller: The charge controller regulates the DC electricity coming from the solar panels to prevent overcharging and damage to the batteries. It ensures the batteries are charged efficiently and safely. There are two main types:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): A cost-effective option for smaller systems.
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking): More efficient, especially in varying sunlight conditions, as it maximizes the power extracted from the solar panels.
- Battery Bank: Batteries store the DC electricity generated by the solar panels. This stored energy is used to power appliances and devices when sunlight is not available (e.g., at night or on cloudy days). Common battery types include:
- Lead-Acid: More affordable initially but require maintenance and have a shorter lifespan. Types include flooded and sealed (AGM and Gel).
- Lithium-Ion (LiFePO4): Higher upfront cost but more efficient, longer-lasting, maintenance-free, and safer.
- Inverter: Most household appliances and electronic devices use alternating current (AC) electricity. The inverter converts the DC electricity stored in the batteries into AC electricity. There are two main types:
- Pure Sine Wave: Provides the highest quality AC power, suitable for sensitive electronics.
- Modified Sine Wave: Less expensive but may not be compatible with all devices.
- Hybrid Inverters: Combine the functions of a charge controller and an inverter.
- Wiring and Mounting: Proper wiring connects all the components, ensuring efficient power flow. Sturdy mounting structures secure the solar panels and optimize their exposure to sunlight.
- Optional Components:
- Backup Generator: Provides a secondary power source during extended periods of low sunlight or high energy demand.
- Monitoring System: Tracks the system’s performance, including energy production, battery levels, and consumption.
- DC Load Center: For directly powering DC appliances.
- AC Load Center: Distributes AC power to various circuits.
- Transfer Switch: Used with a generator to switch between solar and generator power.
Types of off-grid solar power systems:
Off-grid solar power systems can vary depending on their size, complexity, and specific applications. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of off-grid solar power systems:
🌞 1. DC-Only Off-Grid System
- Used for: Very small setups (e.g. cabins, RVs, boats).
- Power type: Direct Current (DC) only.
- Appliances: DC-powered lights, fans, USB chargers.
- Key Components:
- Solar panel
- Charge controller
- Battery (usually 12V or 24V)
✅ Simple, low-cost, and easy to maintain.
❌ Limited to DC appliances only.
⚡ 2. AC-Only Off-Grid System
- Used for: Homes or buildings with standard AC appliances.
- Power type: Alternating Current (AC).
- Key Components:
- Solar panels
- Charge controller
- Battery bank
- Inverter
✅ Supports regular home appliances.
❌ A bit more complex and costly.
🔄 3. AC/DC Hybrid Off-Grid System
- Used for: More flexible or mixed-use setups.
- Power type: Both AC and DC.
- Key Components:
- Solar panels
- Charge controller
- Battery bank
- Hybrid inverter
✅ Can power both types of appliances, ideal for modern setups.
❌ Requires more planning and proper wiring.
🔋 4. Off-Grid System with Generator Backup
- Used for: Areas with frequent low sunlight or high power demand.
- Backup: Diesel, gas, or propane generator.
- Key Components:
- Standard off-grid solar setup
- Generator with automatic transfer switch (optional)
✅ Extra reliability when solar power is low.
❌ Higher maintenance and fuel costs.
🏡 5. Modular or Scalable Off-Grid System
- Used for: Growing needs (like expanding homes, tiny homes, eco-villages).
- Designed to be expanded over time.
- Key Components:
- All standard off-grid components
- Designed with flexibility in mind
✅ Add panels, batteries, or inverters as needed.
❌ Requires good planning from the start.
✅ Advantages of Off-Grid Solar Power Systems:
- Independence from the Utility Grid
- No reliance on the power grid means you’re safe from outages or rising electricity costs.
- Ideal for Remote Locations
- Perfect for rural or isolated areas where grid access is unavailable or expensive to install.
- Environmentally Friendly
- 100% renewable and clean energy source, reducing your carbon footprint.
- Energy Self-Sufficiency
- You produce, store, and manage your own power—total control over your energy use.
- No Electricity Bills
- Once installed, there are no monthly power bills (though maintenance and replacement costs still apply).
❌ Disadvantages of Off-Grid Solar Power Systems:
- High Initial Cost
- Expensive setup due to the need for batteries, inverters, and additional equipment.
- Battery Storage Required
- Energy must be stored for nighttime or cloudy days, and batteries can be costly and require regular replacement.
- Energy Limitations
- Limited power supply means careful energy management is necessary, especially in bad weather or winter months.
- Maintenance Responsibility
- You’re responsible for upkeep, battery replacements, and system troubleshooting—no utility company support.
- Not Ideal for High Energy Demands
- Can struggle to support heavy loads like large appliances or heating systems without a very large (and expensive) system.
In summary, an off-grid solar system captures sunlight, converts it to DC electricity, stores it in batteries, and then inverts it to AC electricity to power homes and appliances independently of the traditional power grid. The sizing of each component depends on the energy needs, location, and budget of the user.