Quad Spacer Damper:
A Quad Spacer Damper is a mechanical device used in overhead high-voltage transmission lines, specifically with quad bundle conductors — that is, four conductors bundled together per phase. Quad Spacer Dampers are to control Aeolian vibration and sub-span oscillation. Also, to maintain conductor spacing and restore conductor spacing after a short circuit occurs.
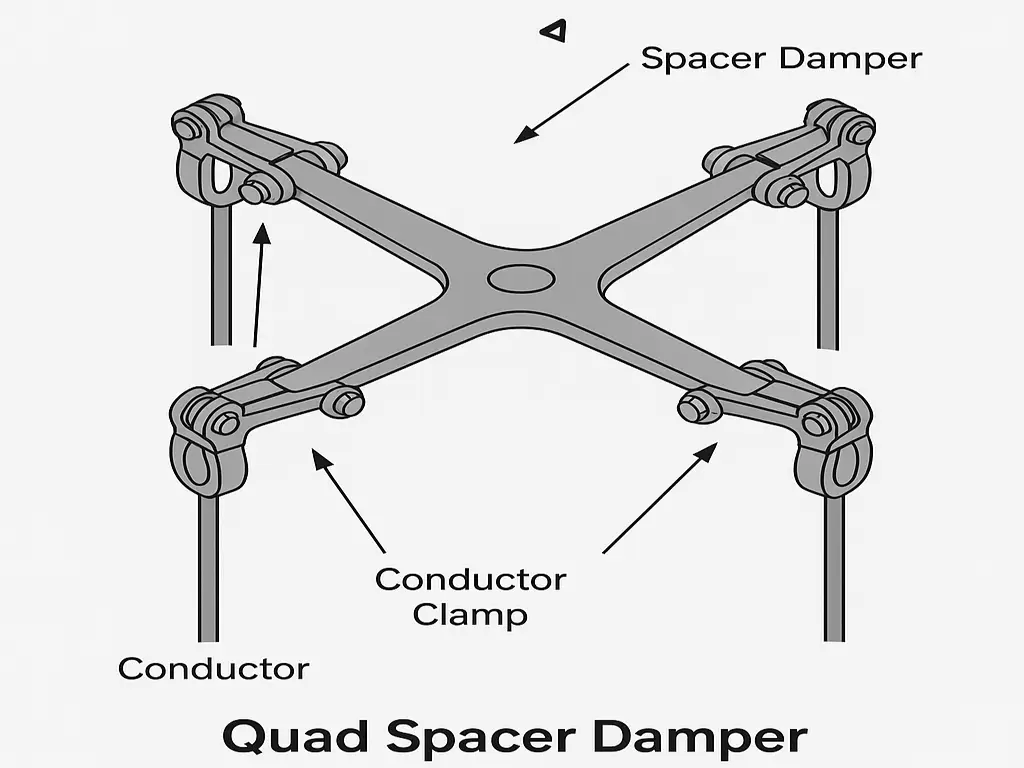
A Quad Spacer Damper is a composite device that:
- Maintains uniform spacing between the four conductors in a quad bundle, and
- Dampens mechanical vibrations caused by wind (like aeolian vibration and galloping).
Function and Importance:
Spacing:
Prevents the four conductors in a bundle from touching or colliding with each other during wind or load-induced motion.
Damping:
Absorbs or dissipates vibration energy, which helps reduce:
- Metal fatigue
- Damage to conductors
- Noise and energy losses
Electrical Performance:
Proper spacing reduces corona discharge and radio interference, improving the overall electrical efficiency.
Mechanical Stability:
Helps ensure the long-term structural integrity of the conductor system.
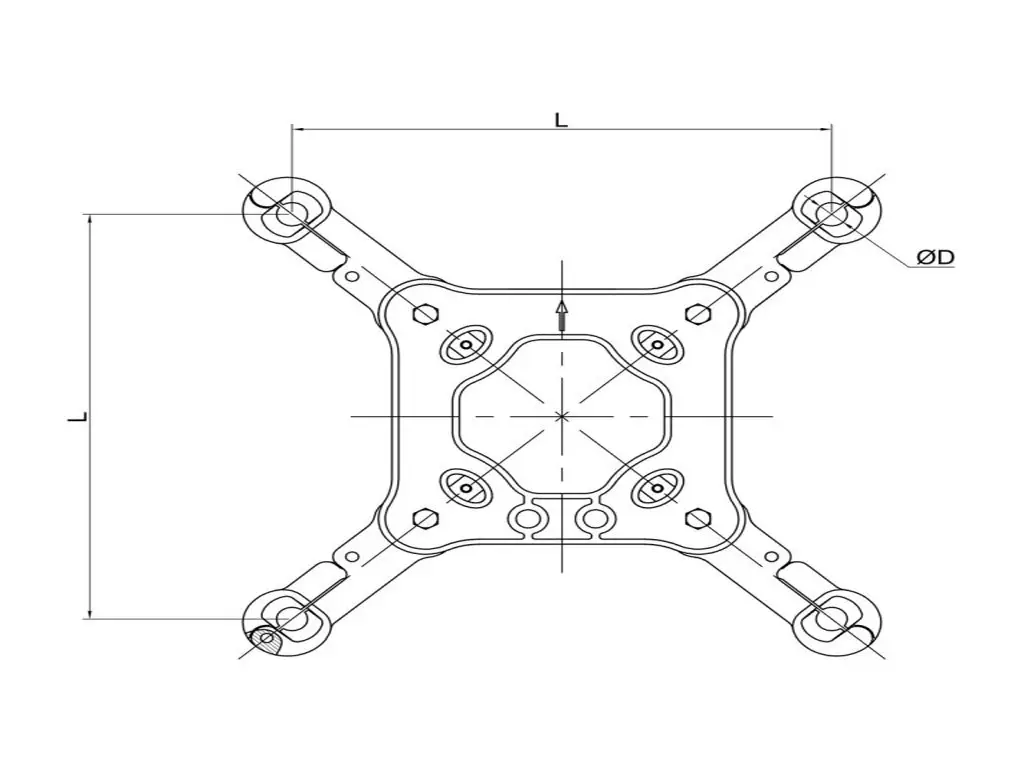
Typical Components:
- Aluminum or composite body
- Rubber or elastomeric damping elements
- Clamps or grips for attaching to each sub-conductor
- Sometimes rotating joints or springs
Where it’s Used:
Used in Extra High Voltage (EHV) and Ultra High Voltage (UHV) transmission lines (220 kV and above), where bundle conductors are essential to:
- Increase current-carrying capacity
- Reduce corona loss
- Minimize reactance
Quad Spacer Damper – Technical Features
| Category | Technical Details |
| Design Purpose | Maintains spacing and provides damping between four subconductors in a bundle |
| Conductor Configuration | Quadruple bundle conductor system |
| Damping Type | Vibration and oscillation damper (for Aeolian vibration, subspan oscillation, galloping) |
| Material – Clamp Body | High-strength aluminum alloy (corrosion-resistant, light-weight) |
| Material – Spacer Arm | Galvanized steel or aluminum alloy arms with elastomeric or polymeric damping inserts |
| Damping Element | High-durability elastomer (EPDM/Silicone rubber) or viscoelastic polymer |
| Fasteners | Stainless steel bolts, washers, and locknuts (corrosion-proof, high torque strength) |
| Applicable Voltage Level | 220 kV, 400 kV, 500 kV, 765 kV, up to 1100 kV (UHV) |
| Clamp Type | Bolt-on or compression type clamps (non-slip, vibration-proof) |
| Conductor Diameter Range | Typically supports 24 mm – 42 mm conductors per bundle (varies by design) |
| Sub-conductor Spacing | 400 mm – 600 mm (typical; can be customized based on line design) |
| Temperature Range | –40°C to +100°C (weather and load tolerant) |
| Corona Resistance | Smooth surface and non-sharp edges to prevent corona discharge |
| Aerodynamic Design | Minimizes wind resistance and ice accumulation |
| Installation Method | Manual or tool-assisted; clamp tightening torque must be strictly maintained |
| Service Life | Typically 25–30 years with minimal maintenance |
| Testing Standards | IEC 61897, IEEE 563, ASTM B117 (salt spray), vibration test standards |
Optional Features
- Damping inserts can be tuned for specific frequency ranges.
- Bird deflector options for lines in rural or migratory zones.
- Color marking or reflector plates for visibility and aviation safety.
Spacer Dampers: Comparison Table
| Feature | Twin Spacer Damper | Triple Spacer Damper | Quad Spacer Damper |
| Number of Conductors | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Used In | 132–220 kV lines | 220–400 kV lines | 400–765 kV or UHV lines |
| Main Purpose | Maintain spacing & damp 2 conductors | Maintain spacing & damp 3 conductors | Maintain spacing & damp 4 conductors |
| Structure | 1 central arm, 2 clamps | 1 central hub, 3 arms/clamps | 1 central hub, 4 arms/clamps |
| Vibration Control | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Corona Reduction | Limited | Better than twin | Excellent |
| Used With | Twin-bundle conductor | Triple-bundle conductor | Quad-bundle conductor |
Why Use Bundled Conductors?
Higher voltage transmission systems (220kV and above) use bundled conductors (2–4 wires per phase) to:
· Damping Aeolian Vibrations
· Mitigating Sub span Oscillations
· Reducing Galloping
· Maintaining Conductor Spacing:
· Increase power transfer capacity
· Minimize corona loss
· Lower reactance and increase efficiency
· Reduce noise and radio interference
1. Damping Aeolian Vibrations
- Cause: Low-amplitude, high-frequency vibrations due to steady, moderate wind (3–15 m/s).
- Effect: Long-term vibration fatigue at suspension points and hardware.
- Spacer Damper Role: Absorbs energy and prevents damage by providing mechanical damping between sub conductors.
2. Mitigating Sub-span Oscillations
- Cause: Vortex shedding between sub conductors, especially on long spans.
- Effect: Oscillations occur within sub-spans, leading to fatigue and eventual failure.
- Spacer Damper Role: Provides internal damping to each sub-span and suppresses resonant behavior.
3. Reducing Galloping
- Cause: Large-amplitude, low-frequency vertical oscillations due to ice/wind asymmetry.
- Effect: Violent conductor movement can cause flashovers, damage, and outages.
- Spacer Damper Role: Adds dynamic stability by resisting vertical oscillation and preventing conductors from coming too close.
4. Maintaining Conductor Spacing
- Importance: Maintains uniform distance between sub conductors, especially in quad or triple bundles.
- Spacer Damper Role: Prevents sub conductors from clashing or tangling during wind or load conditions.
Electrical and Performance Benefits
5. Increases Power Transfer Capacity
- Bundle conductors lower the line’s impedance, which enables transmission of more current without increasing losses.
6. Minimizes Corona Loss
- Corona discharge occurs when electric field intensity is too high.
- Bundle conductors + proper spacing = lower surface voltage gradient → less corona discharge.
7. Lowers Reactance and Increases Efficiency
- Inductive reactance is reduced in bundled conductor’s → lower voltage drop, improved voltage regulation, and higher transmission efficiency.
8. Reduces Noise and Radio Interference
- Proper spacing and damping reduce:
- Audible noise from corona.
- Radio interference from electrical discharge.
Notes:
- Quad spacers are critical for long-span transmission lines to reduce wear and conductor fatigue.
- Proper installation torque and alignment are important for long-term performance.
- In some designs, spacer dampers also include integrated vibration dampers (twin-arm design) to combine both functions.