3 Phase Energy Meter
Definition:
A three-phase energy meter is an electrical device used to measure the consumption of electrical energy in a three-phase system. It is typically used in industrial, commercial, and large residential setups where three-phase electrical power is used for greater efficiency in delivering high amounts of electrical load. The three-phase energy meter tracks the total energy consumption across all three phases and records the electrical usage, usually in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Three-phase meters can also measure other parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and apparent power, depending on their sophistication and features. They are typically equipped with displays or can transmit data remotely for monitoring purposes.
Construction of Three-Phase Energy Meter
The construction of a three-phase energy meter consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in measuring and recording energy consumption accurately. Below are the primary parts of the construction:
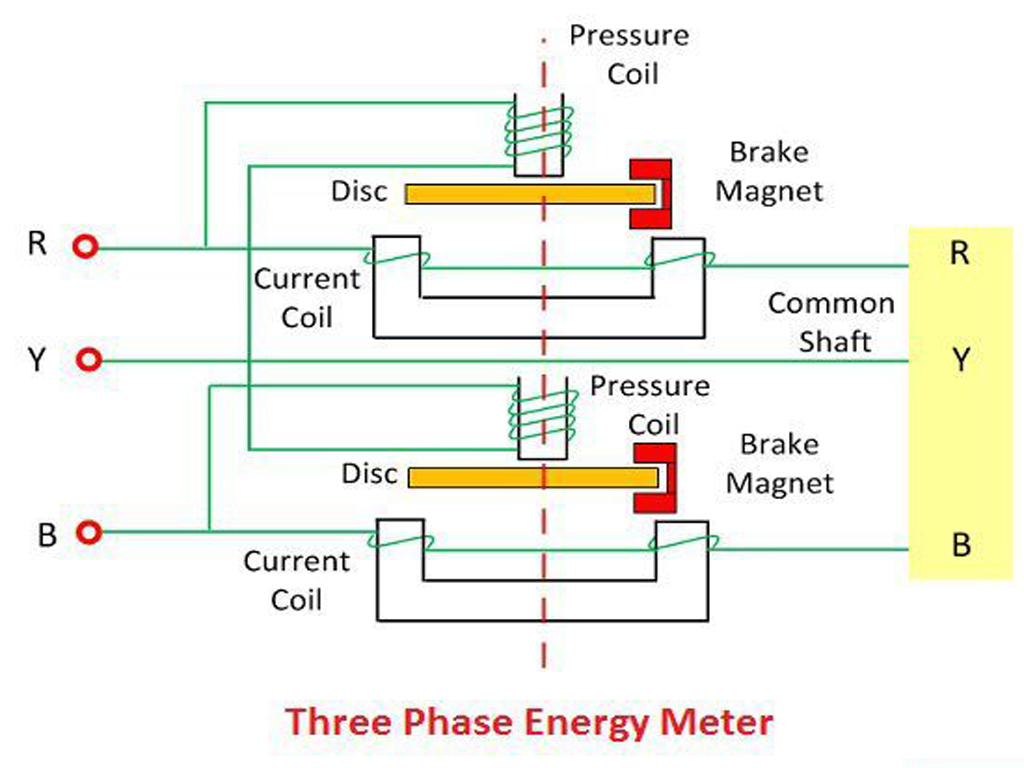
- Electromagnetic Mechanism: This is the core part of the energy meter. It consists of a rotating disk (or rotor) and coils (or electromagnets) that create magnetic fields. The rotation of the disk is proportional to the energy consumed.
- Driving System: This system comprises electromagnets, including current coils and pressure coils. Current coils are connected in series with the load, carrying the load current. Pressure coils are connected across the voltage supply, carrying a current proportional to the voltage.
- Moving System: An aluminum disc is mounted on a shaft, positioned between the electromagnets. The interaction of magnetic fields induces eddy currents in the disc, causing it to rotate.
- Brake Magnet: A brake magnet is placed near the rotating disk to control its speed. This ensures that the disk’s movement is proportionate to the energy consumption and is not too fast or too slow. The brake magnet works by generating a magnetic field that opposes the movement of the disk, providing a constant speed.
- Register or Display: The energy meter includes a register that records the number of rotations of the disk, which is proportional to the energy consumed. In older mechanical meters, this is a set of dials or an analog display. In modern digital meters, it might be a digital display or remote reading system.
- Voltage and Current Transformers (optional): For high-voltage applications, voltage transformers (VTs) and current transformers (CTs) are used to step down the voltage and current to measurable values suitable for the meter.
- Phase Selector or Phase Connection: The three-phase energy meter is designed to be connected to all three phases of the electrical system. It has three inputs corresponding to each phase (R, Y, and B).
Working Principle:
The current flowing through the series coils creates a magnetic field, which induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the shunt coils. This interaction generates a torque on the rotating disk. The magnetic field produced by the current and voltage results in the movement of the disk. The amount of torque depends on the magnitude of the current and voltage in the system. The interaction of these magnetic fields produces a torque that rotates the aluminum disc.
The disk starts rotating, and the speed of rotation is directly proportional to the total power consumed in the three-phase system. The rotation speed varies depending on the load, as the power consumption increases or decreases. A higher load causes the disk to spin faster, indicating more power consumption.
The disk is connected to a mechanical counter or a register. Each rotation of the disk corresponds to a specific amount of energy consumed (measured in kWh). The register accumulates the rotations, providing a direct reading of the total energy consumed over time.
The braking system regulates the disc’s speed, ensuring accurate measurement. The brake magnet adjusts the speed of the rotating disk to make sure the movement remains proportional to the actual power consumption, preventing excessive or uncontrolled rotation. The register, which might be analog or digital, displays the total energy consumption, typically in kilowatt-hours (kWh). In modern meters, digital displays often include more advanced features like power factor, voltage, and current measurement.
Types:
There are electro-mechanical (induction) and electronic (digital) three-phase energy meters. Digital meters are becoming increasingly common due to their advanced features and accuracy.
There are typically two types of 3-phase meters. Let us read more about them!
- Three phases, three wire meters: This system is a combination of two single-phase meters. It uses a permanent horseshoe magnet.
- Three phases, four-wire meter: This system consists of three coils and three aluminum discs. It is suitable for measuring the kWh in a 3-phase motor amps calculation. It functions similar to a three-phase, three-wire electric meter.
Advantages of Three Phase Meter:
- Higher Power Capacity: Three-phase systems, and therefore three-phase meters, are designed to handle significantly larger electrical loads compared to single-phase systems. This makes them essential for powering heavy machinery, industrial equipment, and large commercial buildings.
- Accurate Measurement: Three-phase meters provide precise measurement of energy consumption across all three phases of the electrical supply. This ensures accurate billing and allows for effective monitoring of energy usage.
- Efficient Energy Usage: By accurately tracking energy consumption, three-phase meters enable businesses to identify areas where they can optimize energy usage and reduce costs. Also three phase power delivery is more efficient than single phase power delivery.
- Advanced Features: Modern three-phase meters, especially digital ones, often come with advanced features such as:
- Remote monitoring and communication capabilities.
- Time-of-use metering, which allows for different energy rates at different times of the day.
- The ability to measure both active and reactive power.
- Data logging.
- Stability and Reliability: Three phase power delivers a more consistent power flow, this helps with the stability of machinery that is powered by three phase power.
- Facilitates better power grid management: The data collected by three phase meters, allows utility companies to better manage the power grid.
FAQs:
1. How does a three-phase energy meter work?
Answer: A three-phase energy meter works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It uses current and voltage from all three phases to produce a magnetic field, which causes a rotating disk. The speed of the disk’s rotation is proportional to the energy consumed, and this movement is recorded by the meter to show total energy usage.
2. Why is a three-phase system used instead of a single-phase system?
Answer: A three-phase system is more efficient for high-power applications. It provides a constant flow of power, reduces power loss, and allows for the transmission of more electricity with less current, making it ideal for industrial and commercial applications that require large amounts of power.
3. What is the difference between a single-phase and a three-phase energy meter?
Answer: A single-phase energy meter measures energy consumption in a system with one alternating current, while a three-phase energy meter measures consumption in a three-phase system, which includes three alternating currents. The three-phase system provides a more balanced, efficient power supply, particularly for heavy machinery.
4. Can a three-phase energy meter measure the power factor?
Answer: Yes, modern three-phase energy meters can measure not only the energy consumption but also parameters such as the power factor. This helps to understand the efficiency of the electrical system and to prevent penalties from utility companies for poor power factor.
5. What happens if one of the phases is disconnected or fails?
Answer: If one of the phases in a three-phase system fails or is disconnected, the energy meter may still function, but the readings will be inaccurate, as the system will no longer be balanced. It is important to identify phase imbalances, as they can cause inefficiencies or damage to equipment. Advanced meters can often detect such imbalances.
6. How accurate are three-phase energy meters?
Answer: Three-phase energy meters are highly accurate and designed to provide reliable readings within a specified tolerance range (typically within 1-2%). They are calibrated to measure energy consumption based on the voltage and current of all three phases.
7. Can three-phase energy meters be used for remote monitoring?
Answer: Yes, many modern three-phase energy meters come with advanced features like communication ports, allowing remote monitoring and data collection. These meters can transmit data to a central system or cloud platform, enabling real-time energy consumption tracking and more effective energy management.
Related Terms:
- Creeping in Energy Meter
- Single Phase Energy Meter
- Difference Between Watt-meter & Energy Meter
- Q Meter
- Electromagnetic Flow Meter
- Smart Prepaid meter