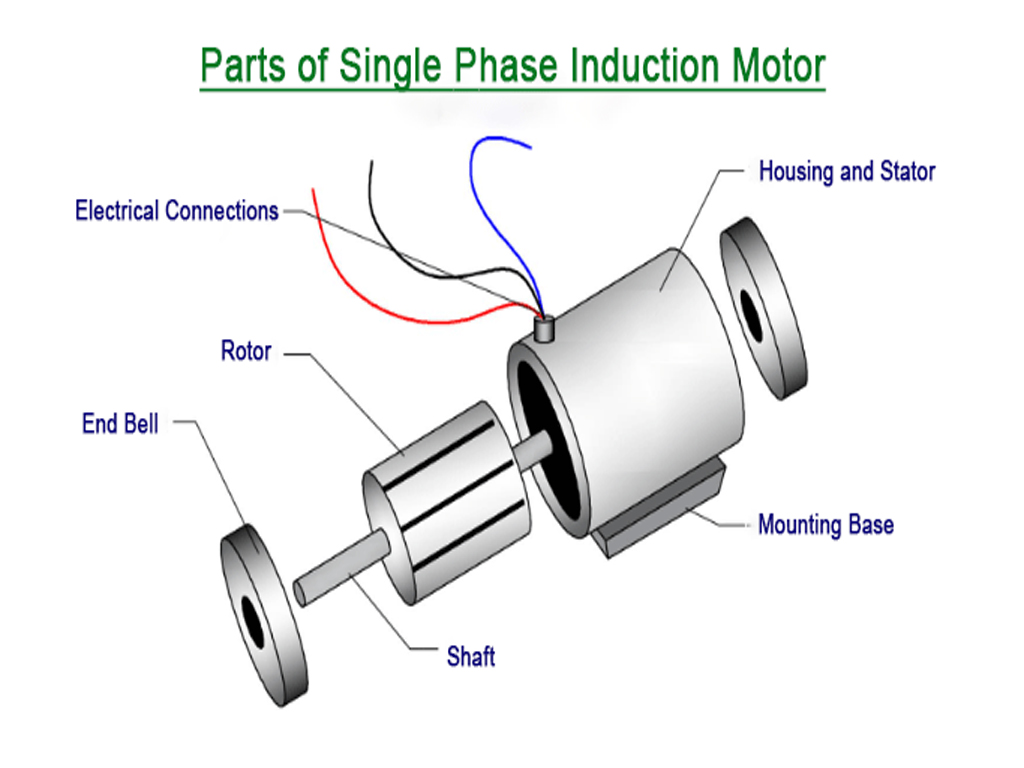
Single-Phase Induction Motor ;
A Single-Phase Induction Motor (SPIM) is one of the most commonly used types of electric motors, especially for small appliances and household applications. It operates on a single-phase AC power supply.
A single-phase induction motor is an AC electric motor that converts single-phase electrical energy into mechanical energy using magnetic interactions. They work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a rotating magnetic field induces current in the rotor, causing it to rotate.
Construction of a Single-Phase Induction Motor:
The basic construction of a single-phase induction motor consists of the following main parts:
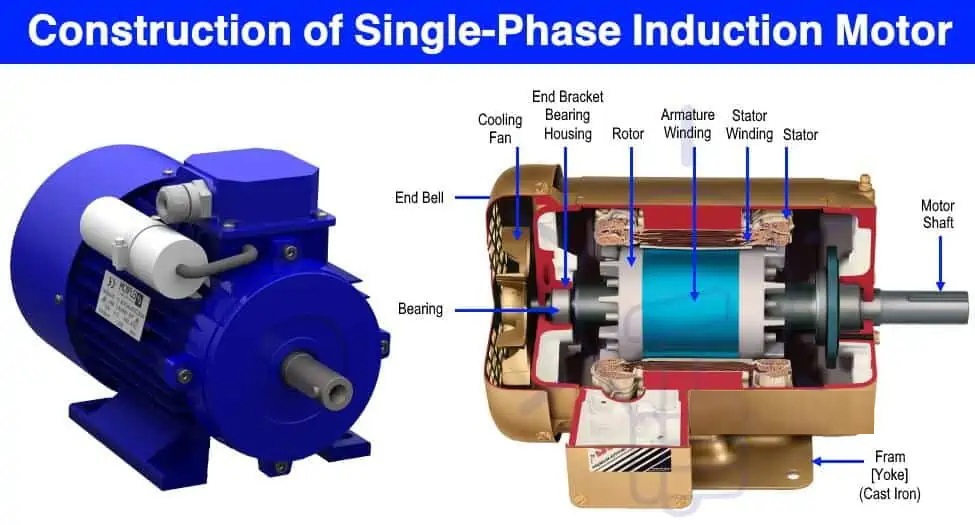
Stator:
The stator is the stationary part of the motor. It is made up of laminated sheets of silicon steel to reduce eddy currents. It has two parts:
- Main winding (or running winding): This winding is powered by the single-phase AC supply.
- Auxiliary winding (or starting winding): This winding is used for starting the motor. It is connected in parallel with the main winding but is typically connected through a capacitor or a centrifugal switch.
Rotor:
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and is located inside the stator. It is usually a squirrel cage type (squirrel cage rotor) consisting of laminated conductors shorted at both ends by conducting rings.
End Bells:
End bells cover the ends of the stator and rotor. They support bearings that allow the rotor to rotate.
Bearings:
Bearings support the rotor shaft and enable smooth rotation.
Working Principle of a Single-Phase Induction Motor:
A single-phase induction motor works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which states that a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force (Lorentz force).
Key Working Steps:
- When an AC current flows through the stator winding, it produces a rotating magnetic field.
- However, a single-phase AC supply creates only a pulsating magnetic field, which is not a rotating magnetic field. To overcome this, the auxiliary winding and capacitor (in some motors) are used to create a phase difference, making the overall magnetic field appear to rotate.
- The rotating magnetic field induces current in the rotor conductors, and according to Faraday’s Law of Induction, this induces a torque that causes the rotor to rotate.
- Once the motor starts running, it behaves like a three-phase induction motor.
Types of Single-Phase Induction Motors:
Split-Phase Motor:
- The most common type of single-phase induction motor.
- It uses two windings: a main winding (running winding) and an auxiliary winding (starting winding).
- A centrifugal switch disconnects the auxiliary winding after the motor reaches a certain speed.
Capacitor-Start Motor:
- Has a capacitor in series with the starting winding to improve starting torque.
- The motor is disconnected from the capacitor once it reaches full speed (via a centrifugal switch).
Capacitor-Run Motor:
- A capacitor is permanently connected to the auxiliary winding during the motor’s operation.
- Provides better efficiency and continuous running performance.
Shaded Pole Motor:
- A simple design with a shaded pole to create a rotating magnetic field.
- Generally used in low-power applications (e.g., small fans and toys).
Permanent-split capacitor (PSC) motors:
- Use a single capacitor for both starting and running.
Advantages:
- Simple construction.
- Relatively low cost.
- Self-Starting.
- Reliable and require minimal maintenance.
- Suitable for household appliances.
- They are widely available and used in various household appliances, small tools, and industrial applications.
Disadvantages:
- Low starting torque.
- Lower efficiency compared to three-phase induction motors.
- Generally lower power ratings.
- Speed control is more difficult compared to other types of motors like DC motors or three-phase motors.
Applications of Single-Phase Induction Motors:
Household Appliances:
- Fans
- Washing machines
- Refrigerators
- Air conditioning units
Small Tools:
- Drills
- Blowers
- Pumps (in small capacities)
HVAC Systems:
- Small air handling units
- Exhaust fans
- Ventilation systems
Office Equipment:
- Shredders
- Printers
- Copy machines
Pumps and Compressors:
Small water pumps, oil pumps, and compressors used in homes or small industries.
Sewing Machines and Other Light Machinery:
In textiles and other small machinery, where power requirements are low.