Introduction:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly growing field that focuses on creating systems capable of performing tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as learning, decision-making, problem-solving and pattern recognition. In Electrical Engineering, AI has become an important tool for improving the efficiency, reliability and automation of electrical systems.
With the increasing complexity of modern electrical networks, traditional methods are often insufficient to handle large amounts of data and dynamic operating conditions. AI techniques such as machine learning, neural networks, fuzzy logic and expert systems enable electrical engineers to analyze data more accurately, predict system behavior and make intelligent decisions in real time.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is widely used in areas such as power systems, smart grids, electrical machines, renewable energy systems, industrial automation and fault diagnosis. For example, AI-based algorithms can predict electrical load demand, detect faults in transmission lines, optimize energy consumption and control motors more efficiently.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence in Electrical Engineering helps reduce human intervention, minimize errors, improve system performance and enhance safety. As technology continues to advance, AI is expected to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of electrical engineering by enabling smarter, more adaptive and energy-efficient systems.
Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Power Systems Analysis
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a vital role in modern power systems analysis by enhancing the accuracy, speed and efficiency of system monitoring, operation and decision-making. Traditional power system analysis methods often struggle to handle the complexity, uncertainty and large volume of data generated by modern electrical networks. AI techniques provide intelligent solutions to these challenges.
AI algorithms such as machine learning, neural networks and fuzzy logic are widely used for analyzing power system behavior under different operating conditions. These techniques help in load forecasting, voltage stability analysis, contingency analysis and fault detection. By learning from historical and real-time data, AI models can predict system performance more accurately than conventional methods.
In power system operation, AI supports real-time monitoring and control, enabling faster detection of abnormal conditions such as overloads, voltage drops and equipment failures. AI-based systems can analyze complex patterns and provide early warnings, helping operators take preventive actions and reduce the risk of blackouts.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) also improves power system planning and optimization by assisting in generation scheduling, network expansion and energy management. With the integration of renewable energy sources, AI helps manage uncertainty and variability, ensuring stable and reliable power supply.
Overall, the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in power systems analysis is to make electrical networks smarter, more reliable and more efficient, supporting the development of modern, intelligent power grids.
AI Applications in Smart Grid Technology
Smart grid technology represents the modernization of traditional power systems by integrating digital communication, automation and advanced control. Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in making smart grids truly “intelligent” by enabling systems to learn from data, adapt to changing conditions and make autonomous decisions in real time.
One of the most important AI applications in smart grids is intelligent demand response management. AI algorithms analyze consumer usage patterns, weather data and time-based demand to predict peak load conditions. Based on these predictions, the smart grid can automatically adjust power distribution or encourage consumers to shift usage, reducing peak demand and preventing system overloads.
AI is also widely used for real-time fault detection and self-healing in smart grids. Using data from sensors, smart meters and protection devices, AI systems can quickly identify faults, determine their location, and isolate affected sections of the grid. In many cases, AI enables automatic reconfiguration of the network, restoring power without human intervention and significantly reducing outage duration.
Another key application is renewable energy integration. Smart grids must handle the variability of renewable sources such as solar and wind. AI helps forecast renewable generation, balance supply and demand and optimize energy storage systems. This ensures grid stability while increasing the use of clean energy.
AI-driven predictive maintenance is also essential in smart grid technology. By continuously monitoring equipment condition, AI can predict failures before they occur. This reduces unexpected breakdowns, lowers maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of grid assets such as transformers, circuit breakers and transmission lines.
Additionally, AI enhances cybersecurity and energy management in smart grids. Intelligent algorithms can detect abnormal data patterns that indicate cyberattacks or system misuse, ensuring safe and reliable operation. AI-based energy management systems optimize power flow, reduce losses, and improve overall efficiency.
In summary, Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications in smart grid technology enable automation, reliability, efficiency, and sustainability. By transforming raw data into intelligent actions, AI makes smart grids capable of meeting the demands of modern energy systems and future power networks.
🔹 How AI Works in Smart Grid Technology
1. Data Collection from the Grid
Smart grids continuously collect data from:
- Smart meters
- Sensors
- Substations
- Renewable energy sources
- Energy storage systems
This data includes voltage, current, frequency, power demand, weather conditions, and equipment status.
2. Data Processing and Analysis
The collected data is filtered and processed to remove noise and errors.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems analyze this data to understand:
- Load patterns
- Demand variations
- Grid operating conditions
3. Learning and Pattern Recognition
AI algorithms such as Machine Learning and Neural Networks learn from historical and real-time data.
They identify:
- Normal operating behavior
- Abnormal conditions
- Trends and correlations
This learning ability allows the grid to adapt to changing conditions.
4. Prediction and Forecasting
Artificial Intelligence (AI) predicts:
- Electricity demand (load forecasting)
- Renewable energy generation (solar/wind)
- Possible faults or failures
Accurate prediction helps prevent overloads and blackouts.
5. Intelligent Decision Making
Based on analysis and predictions, AI automatically decides:
- Power generation scheduling
- Load balancing
- Energy storage charging/discharging
- Demand response actions
These decisions optimize efficiency and reliability.
6. Control and Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) sends control commands to:
- Substations
- Switchgear
- Inverters
- VFDs
This enables real-time automation, self-healing, and fast fault isolation.
7. Feedback and Continuous Learning
The grid’s response is monitored and fed back into the AI system.
AI continuously improves its performance through learning.
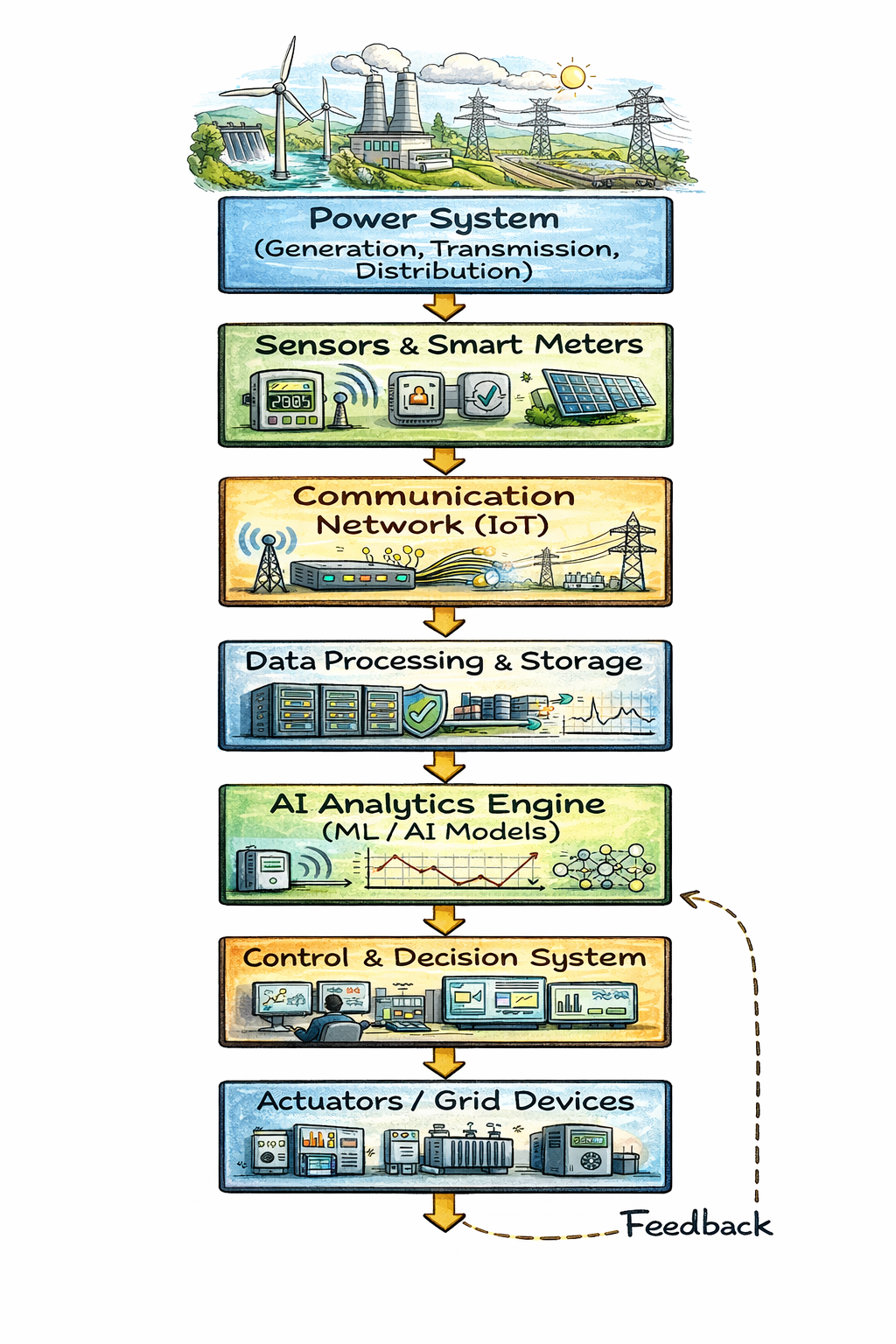
🔹 Main Components of AI-Based Smart Grid Technology
1. Smart Meters
Measure real-time energy consumption and send data to the grid operator.
2. Sensors and Monitoring Devices
Installed across transmission and distribution networks to monitor:
- Voltage
- Current
- Frequency
- Temperature
3. Communication Network
Transfers data between grid components using:
- Fiber optics
- Wireless networks
- IoT technology
4. AI Analytics Platform
This is the core intelligence where:
- Data is analyzed
- Predictions are made
- Control decisions are generated
Uses ML, AI, and big data techniques.
5. Control Centers
Grid operation centers where AI systems manage:
- Load dispatch
- Fault handling
- Grid optimization
6. Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Includes:
- Solar panels
- Wind turbines
- Energy storage systems
AI manages their integration and variability.
7. Power Electronic Devices
Such as:
- Inverters
- VFDs
- FACTS devices
AI controls these to regulate power flow and voltage.
8. Cybersecurity Systems
Artificial Intelligence (AI) monitors data patterns to detect:
- Cyberattacks
- Unauthorized access
- Abnormal behavior
🔹 Advantages of AI in Smart Grid Technology
- Improved reliability and stability
- Faster fault detection and recovery
- Efficient energy management
- Better renewable integration
- Reduced power losses
- Enhanced consumer participation
Machine Learning for Load Forecasting
Load forecasting is one of the most critical tasks in power system operation and planning, as it directly affects generation scheduling, grid stability and energy costs. Machine Learning (ML) has transformed load forecasting by providing data-driven models that can learn complex patterns in electricity consumption more accurately than traditional statistical methods.
Machine learning models use historical load data combined with weather conditions, calendar effects and consumer behavior to predict future electricity demand. Factors such as temperature, humidity, day of the week, holidays and seasonal trends strongly influence load variation. ML algorithms can automatically identify these relationships and adapt when consumption patterns change over time.
Different machine learning techniques are used for different forecasting horizons. Short-term load forecasting (minutes to hours ahead) often uses models like artificial neural networks, support vector machines and decision trees to support real-time grid operation. Medium-term and long-term forecasting rely on regression models, ensemble learning and deep learning techniques to support maintenance planning, capacity expansion and energy policy decisions.
One major advantage of machine learning is its ability to handle nonlinear and uncertain data. Unlike traditional forecasting methods, ML models improve continuously as new data becomes available. This makes them especially effective in modern power systems with renewable energy integration, electric vehicles and smart appliances, where load behavior is highly dynamic.
Machine learning-based load forecasting also helps reduce operational costs and energy losses. Accurate demand prediction allows utilities to optimize generation dispatch, minimize reserve margins and reduce reliance on expensive peaking power plants. It also improves reliability by preventing overloads and voltage instability.
In practical applications, ML-driven load forecasting is integrated into Energy Management Systems (EMS) and Smart Grid platforms, enabling automated decision-making and real-time control. As power systems become more complex, machine learning continues to play a vital role in creating efficient, reliable and sustainable electricity networks.
Overall, machine learning for load forecasting provides higher accuracy, adaptability and intelligence, making it an essential technology for modern and future power systems.
AI-Based Fault Detection and Diagnosis
Fault detection and diagnosis are critical tasks in electrical engineering, as undetected faults can lead to equipment damage, power outages, safety hazards, and high maintenance costs. AI-based fault detection and diagnosis use intelligent algorithms to automatically identify, analyze and locate faults in electrical systems more accurately and faster than traditional methods.
In conventional systems, fault detection often relies on fixed thresholds, manual inspection, or rule-based logic, which may fail under complex or changing operating conditions. AI overcomes these limitations by learning patterns from historical data, real-time sensor measurements, and operational behavior. Machine learning models such as neural networks, support vector machines, decision trees and deep learning algorithms can recognize abnormal patterns that indicate early-stage faults.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) -based fault detection is widely applied in power transmission lines, transformers, motors, generators and industrial electrical panels. For example, AI systems can analyze voltage, current, temperature, vibration and partial discharge data to detect insulation degradation or internal faults before a failure occurs. This enables predictive maintenance, reducing unexpected breakdowns and downtime.
Fault diagnosis goes a step further by identifying the type, location and severity of the fault. AI models compare real-time data with learned fault signatures to determine whether a problem is caused by short circuits, overloads, phase imbalance, sensor failure or mechanical issues. This helps maintenance teams respond quickly with the correct corrective action.
Another major advantage of AI-based systems is their ability to operate in real time and adapt continuously. As more data is collected, the AI model improves its accuracy and reliability. This is especially important in modern power systems with renewable energy sources, variable loads and complex automation.
Overall,Artificial Intelligence (AI) -based fault detection and diagnosis enhance system reliability, safety and efficiency. By enabling early fault identification and precise diagnosis, AI reduces maintenance costs, prevents major failures and supports the development of smarter, more resilient electrical systems.
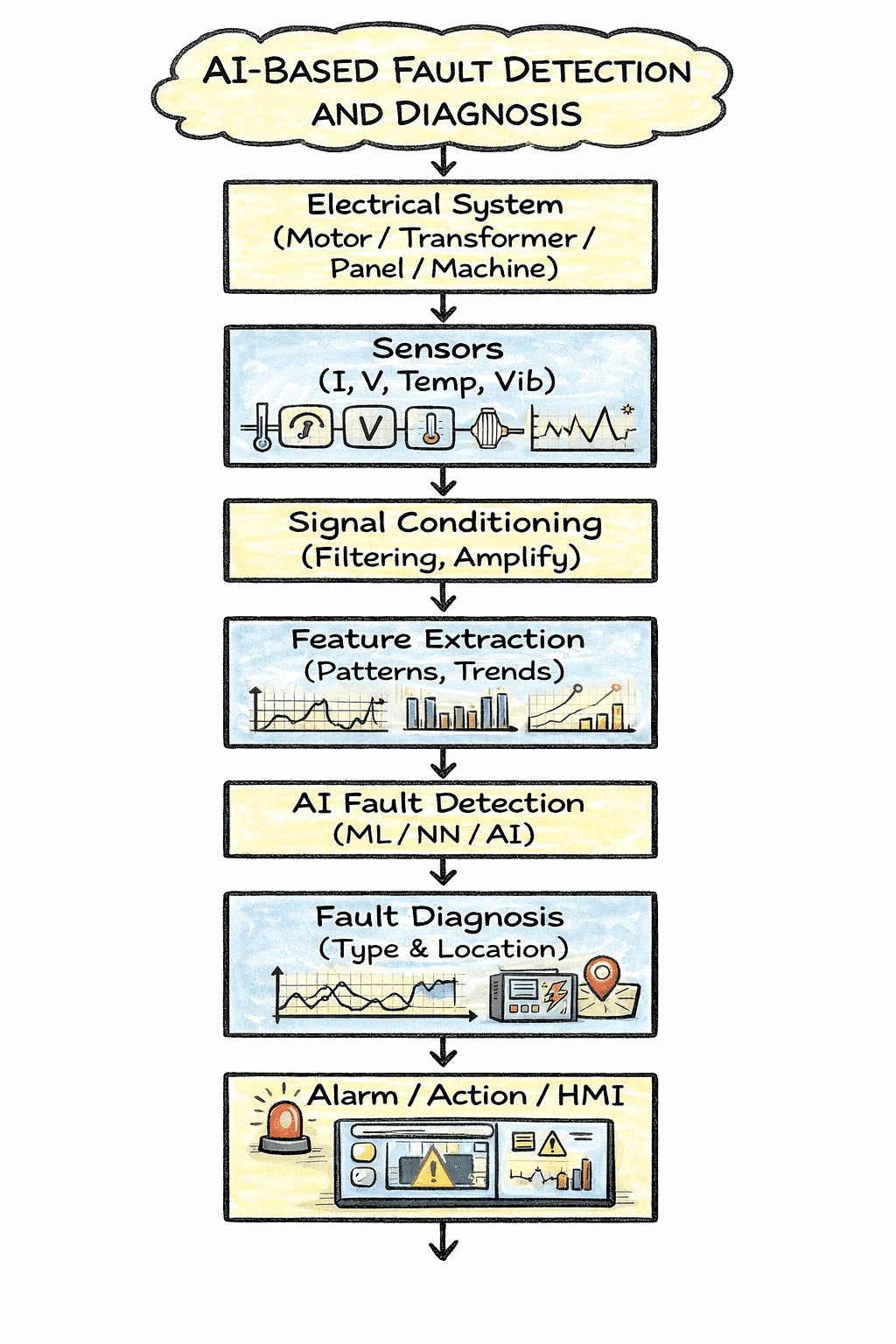
1. Electrical System
This block represents the equipment being monitored, such as a motor, transformer, generator, or electrical panel. Faults may occur in this system during operation.
2. Sensors
Sensors continuously measure electrical and mechanical parameters such as:
- Current (I)
- Voltage (V)
- Temperature
- Vibration
These measurements provide real-time data about the system’s condition.
3. Signal Conditioning
The raw signals from sensors may contain noise or fluctuations.
Function:
- Removes noise
- Amplifies weak signals
- Produces stable and usable data for analysis
4. Feature Extraction
In this stage, important information is extracted from the processed signals.
Examples:
- Abnormal current patterns
- Temperature rise trends
- Vibration frequency changes
These features help the AI system understand system behavior.
5. AI Fault Detection
This is the intelligent part of the system.
Uses:
- Machine Learning
- Neural Networks
- AI algorithms
Function:
- Compares normal and abnormal patterns
- Detects faults at an early stage
6. Fault Diagnosis
After a fault is detected, this block determines:
- Type of fault (overload, short circuit, insulation failure, bearing fault)
- Location of the fault
- Severity of the fault
This helps in accurate troubleshooting.
7. Alarm / Action / HMI
This block communicates fault information to the operator.
Functions:
- Displays fault details on HMI
- Generates alarms or warnings
- Initiates protective actions or system shutdown if required
Overall Working Principle
- Sensors collect real-time data from the electrical system.
- Signals are conditioned and important features are extracted.
- AI algorithms detect abnormal conditions.
- Fault diagnosis identifies the type and location of the fault.
- Alarms or control actions are generated.
How Artificial Intelligence Controls Electrical Machines
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly transformed the way electrical machines such as motors, generators, and drives are controlled. Traditional machine control methods rely on fixed mathematical models and preset parameters, which often struggle to maintain performance under changing load, speed, and environmental conditions. AI-based control introduces adaptability, learning capability, and intelligent decision-making into electrical machine control systems.
🔹 Main Components of Artificial Intelligence (AI) -Based Electrical Machine Control
1. Electrical Machine
This is the controlled system, such as:
- Induction Motor
- Synchronous Motor
- DC Motor
- Servo Motor
The machine provides real-time operational data like speed, torque, current, and temperature.
2. Sensors and Signal Acquisition
Sensors collect real-time feedback from the machine:
- Current sensors
- Voltage sensors
- Speed or position sensors
- Temperature and vibration sensors
These signals are essential for AI models to understand machine behavior.
3. Power Electronic Drive (VFD / Inverter)
The drive controls the electrical supply to the machine by adjusting:
- Voltage
- Frequency
- Current
AI sends control commands to the drive to regulate motor speed, torque, and direction.
4. AI Controller (Core Component)
This is the intelligence of the system, implemented using:
- Neural Networks
- Machine Learning models
- Fuzzy Logic
- Adaptive control algorithms
The AI controller processes input data, predicts behavior, and decides optimal control actions.
5. Control Unit (PLC / Microcontroller / DSP)
This unit executes the AI control logic in real time.
It interfaces between:
- Sensors
- AI algorithm
- Power electronic drive
6. Feedback and Monitoring System
Provides continuous feedback for:
- Performance evaluation
- Fault detection
- System learning and improvement
7. Human–Machine Interface (HMI)
Used for:
- Monitoring machine status
- Setting parameters
- Viewing alarms and diagnostics
🔹 Controlling Steps of AI-Based Electrical Machine Control
Step 1: Data Collection
Sensors continuously collect real-time data such as current, voltage, speed, torque, and temperature from the electrical machine.
Step 2: Data Processing
The collected data is filtered, normalized, and prepared for analysis to remove noise and ensure accurate AI decision-making.
Step 3: AI Model Analysis
The AI algorithm analyzes the processed data to:
- Identify machine operating conditions
- Predict future behavior
- Detect abnormal patterns or faults
Step 4: Decision Making
Based on analysis, the AI controller determines:
- Required speed or torque
- Optimal voltage and frequency
- Corrective actions for disturbances
Step 5: Control Signal Generation
The AI controller generates control signals and sends them to the inverter or drive system.
Step 6: Actuation
The power electronic drive adjusts motor input parameters, controlling:
- Speed
- Torque
- Direction
- Efficiency
Step 7: Feedback Evaluation
The system monitors the machine response and compares it with the desired output.
Step 8: Learning and Adaptation
The AI model updates itself using feedback data, improving accuracy and adapting to:
- Load changes
- Aging components
- Environmental variations
Advantages of AI-Based Control
- Self-learning and adaptive behavior
- Reduced need for manual tuning
- Improved efficiency and reliability
- Early fault detection and protection
- Better performance under variable conditions
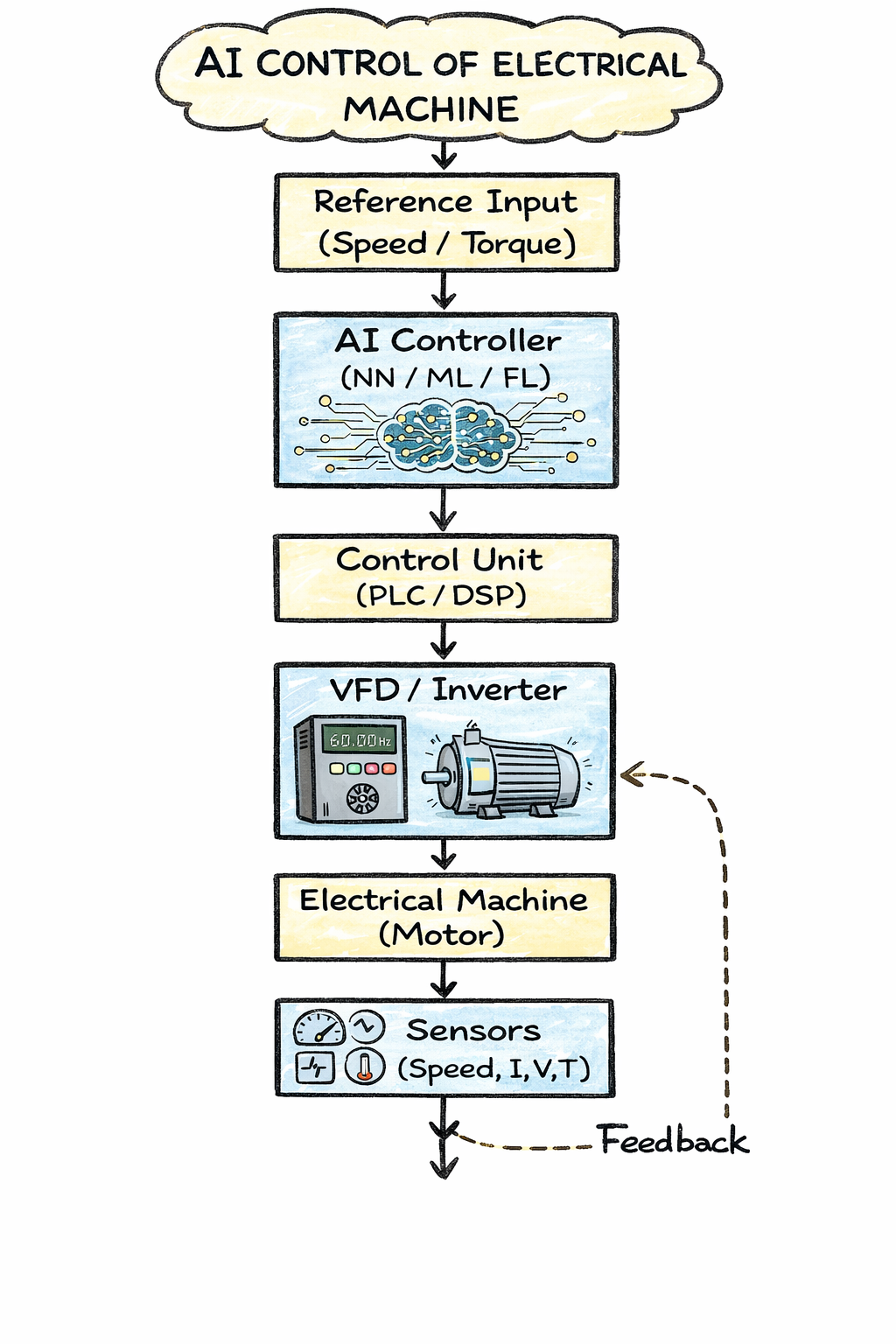
- Reference Input
This block represents the desired value given to the system, such as:
- Required speed
- Required torque
It tells the system how the motor should run.
- AI Controller
This is the brain of the system.
It uses Artificial Intelligence techniques such as:
- Neural Networks
- Machine Learning
- Fuzzy Logic
Function:
- Compares reference input with feedback
- Learns machine behavior
- Decides the best control action
Unlike conventional controllers, it can adapt automatically to load changes.
- Control Unit (PLC / DSP / Microcontroller)
This block converts AI decisions into real electrical control signals.
Function:
- Executes control logic
- Sends command signals to the inverter
- Works in real time
It acts as a link between software and hardware.
- VFD / Inverter
This block controls the power supply to the motor.
Function:
- Changes voltage
- Changes frequency
- Controls current
By doing this, it controls:
- Motor speed
- Motor torque
- Direction of rotation
- Electrical Machine (Motor)
This is the actual load-driving device, such as:
- Induction motor
- Synchronous motor
It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Sensors
Sensors continuously measure:
- Speed
- Current
- Voltage
- Temperature
These signals show the actual condition of the motor.
- Feedback Path
The sensor data is sent back to the AI controller.
Purpose:
- Compare actual output with desired output
- Detect errors
- Improve control accuracy
This feedback makes the system self-learning and intelligent.