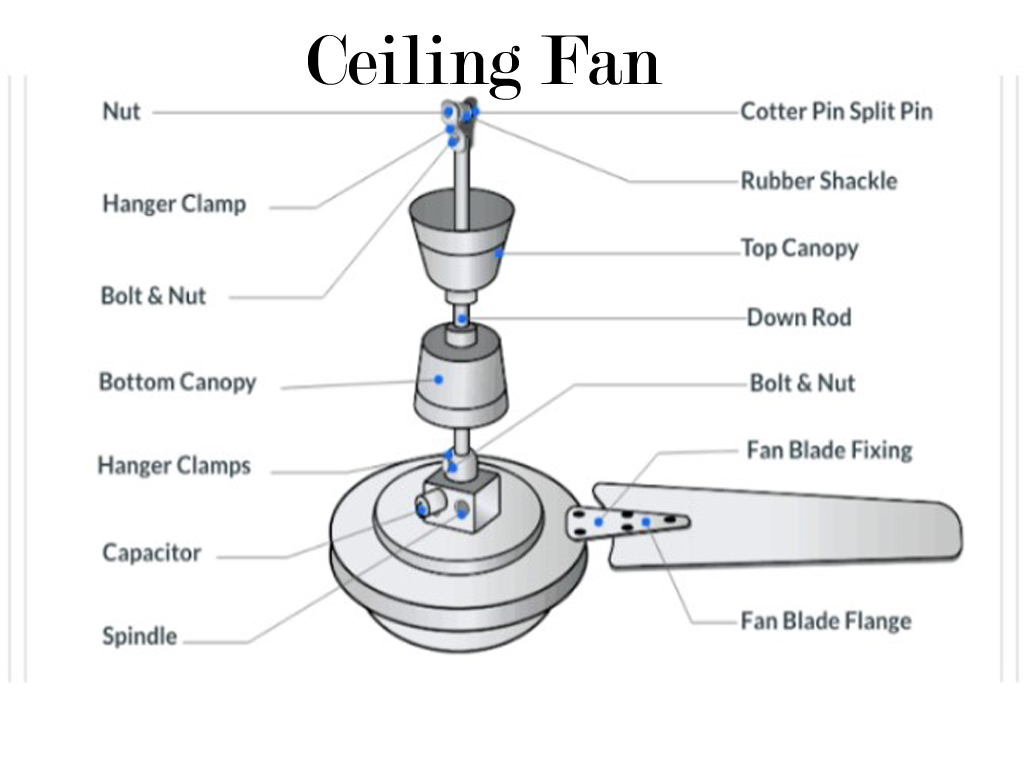
Basic Concept:
What is meant by voltage?
Voltage, also known as electrical potential difference, It represents the difference in electric potential between two points. In simpler terms, it’s the “pressure” that pushes electric charges (electrons) through a conductor, like a wire.
Voltage is measured in volts (V), and it is typically created by a power source such as a battery or a generator.
What is meant by current?
Answer: Current refers to the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire, due to a voltage (or potential difference) across that conductor. It is the rate at which electric charges move through a given point in a circuit.
Measured in Amperes (A), The unit of electric current is the ampere (A), often abbreviated as amp. One ampere is defined as the flow of one coulomb of charge per second.
1 A=1 coulomb/second
Types of Current:
Direct Current (DC): The current flows in one direction only. This is typical of batteries and most electronic devices.
Alternating Current (AC): The direction of current alternates periodically. AC is used in most household electrical outlets (in many countries, this changes direction 50 or 60 times per second, depending on the region).
What is meant by charge?
Answer: Charge refers to a fundamental property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electric and magnetic field. It is the property responsible for electric phenomena and is what drives the flow of current in a circuit.
There are two types of charge:
- Positive charge
- Negative charge
- Electrons carry a negative charge.
- Protons carry a positive charge.
- Neutrons have no charge (they are neutral).
Charge in Electrical Circuits:
- In a circuit, electric charge flows through a conductor when a voltage is applied, and this flow of charge is what we call electric current.
- The amount of charge that flows is related to the current and the time for which it flows. The relationship is: Q=I×t where:
- Q is the total charge (in coulombs),
- I is the current (in amperes),
- t is the time (in seconds) for which the current flows
What is Electricity?
Answer: Electricity is a phenomenon by which an object acquires the property of attracting light objects. The electricity cannot be seen but its effects can be seen.
What do meant by phase and neutral in electrical system?
Answer: 1. Phase (Live or Hot Wire):
The phase wire, also known as the live wire or hot wire, carries the alternating current (AC) from the power source to electrical devices and appliances. The phase wire is the source of electrical energy that powers devices. In an AC system, the voltage in the phase wire alternates between positive and negative, typically changing direction 50 or 60 times per second, depending on the country (this is known as the frequency, measured in hertz, Hz).
The phase wire is usually colored red, or brown (depending on local wiring standards). It is at a high potential compared to the neutral wire, meaning it has a voltage relative to the neutral (usually 120V or 230V depending on the country
2. Neutral Wire:
The neutral wire completes the electrical circuit by providing a return path for the current. It is connected to the ground at the electrical panel (in most systems), so it is generally at zero voltage or earth potential. The neutral wire ensures that the current can flow back from appliances and devices, completing the loop with the phase wire. In standard residential electrical systems, the neutral wire is usually colored black or blue (though the color coding may vary by country).
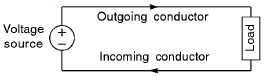
6. What is Basic Circuit?
Answer: It consists of the following: (i) source, (ii) connecting wires, and (iii) load. Figure shows a basic circuit.
7. What is Resistance?
Answer: Resistance: A material’s tendency to resist the flow of charge, measured in ohms (R or Ω). Materials with low resistance are good conductors of electricity, while materials with high resistance are poor conductors.
8. What is meant by electrical power?
Answer: Electrical power refers to the rate at which electrical energy is consumed, produced, or transferred in a circuit or electrical system. The standard unit of electrical power is the watt (W), which represents 1 joule per second (J/s). The general formula for electrical power is:
P=V×I
Where:
- P is power (in watts, W),
- V is voltage (in volts, V),
- I is current (in amperes, A).
What is earthing in an electrical system?
Answer: Earthing is the process of transferring the immediate discharge of the electricity directly to the earth with the help of the low resistance wire. Earthing is used to protect you from an electric shock. It does this by providing a path (a protective conductor) for a fault current to flow to earth. It also causes the protective device (either a circuit-breaker or fuse) to switch off the electric current to the circuit that has the fault.
What is Electrical grounding?
Answer: sometimes called earthing, is the process of connecting to the Earth’s electrical energy. Electrical grounding is the process of directing excess electricity to the ground via a wire. Known as a grounding wire, it’s an essential safety component in most electrical systems. Grounding and earthing is the same term in electrical systems.