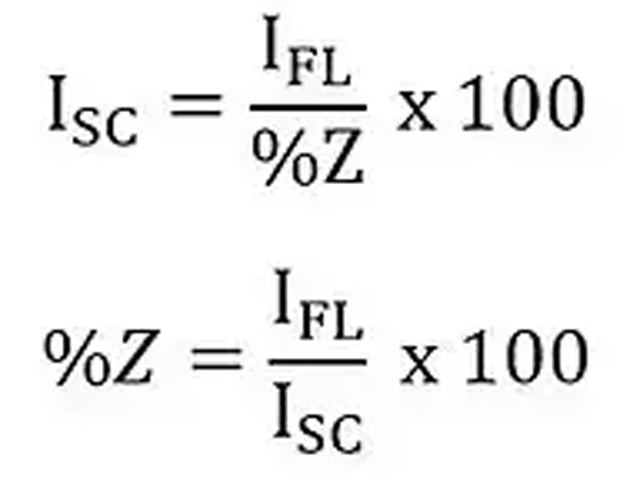What is the percentage impedance of a transformer?
Answer: The percentage impedance of a transformer is a measure of the transformer’s internal impedance (the combination of its resistance and reactance), expressed as a percentage of its rated voltage. It is an important parameter used in system design, fault analysis, and short-circuit calculations.
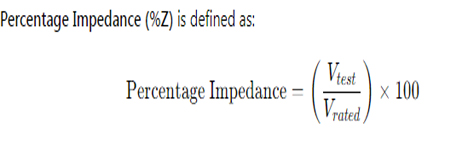
Where:
- Vtest is the voltage required to circulate full-load current through the transformer windings when the secondary is short-circuited.
- Vrated is the rated voltage of the transformer (usually the primary voltage).
- This test is called the short-circuit test.
Interpretation:
- If a transformer has 5% impedance, it means that applying 5% of the rated voltage to the primary side (with the secondary shorted) will produce full-load current.
- It also implies that under fault conditions, the maximum short-circuit current is limited by this impedance.
How it’s calculated:
The percentage impedance is typically determined through a short-circuit test. In this test:
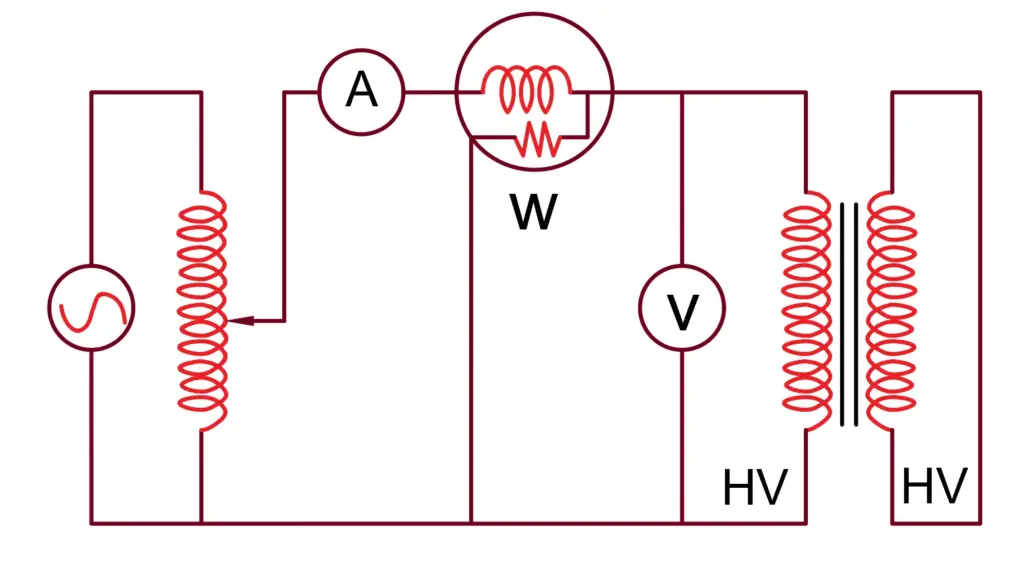
- The secondary winding of the transformer is short-circuited.
- A reduced voltage (short-circuit voltage, VSC) is applied to the primary winding.
- This voltage is gradually increased until the rated current (Irated) flows through the primary winding.
- The percentage impedance is then calculated using the formula:
% Z of transformer =( Vsc/Vrated) X 100
Where:
- VSC is the short-circuit voltage applied to the primary winding.
- Vrated is the rated primary voltage of the transformer.
Significance and Importance:
The percentage impedance is highly significant in transformer applications for several reasons:
- Fault Current Calculation: It is a critical factor in determining the maximum available short-circuit current in a power system. A lower percentage impedance means a higher potential short-circuit current, which requires more robust protective devices.
- Voltage Regulation: It influences the voltage drop across the transformer under load conditions. Transformers with lower impedance generally have better voltage regulation (less voltage drop) but contribute to higher fault currents.
- Parallel Operation: When operating transformers in parallel, it is essential that they have similar percentage impedances (within a certain tolerance, typically +/- 7.5% to 10%). This ensures proper load sharing between the transformers and prevents circulating currents that can lead to overheating and inefficient operation.
- System Design and Coordination: Engineers use the percentage impedance to design and coordinate protection schemes within electrical systems, ensuring that protective devices (like circuit breakers and fuses) can safely interrupt fault currents.
- Efficiency: While not a direct measure of efficiency, impedance does indirectly impact efficiency. Lower impedance can sometimes lead to lower losses, but a very low impedance can also lead to higher inrush currents during energization, which can be problematic.
Factors Influencing Percentage Impedance:
Several design factors influence the percentage impedance of a transformer:
- KVA Rating: Generally, as the kVA rating of a transformer increases, its percentage impedance tends to increase.
- Number of Turns: More turns in the windings typically lead to higher impedance.
- Core Material and Size: The type of core material, its size, and the core’s magnetic properties affect the impedance, particularly the reactance component.
- Winding Arrangement and Geometry: The physical arrangement of the primary and secondary windings, and the distance between them, significantly impact the leakage reactance, and thus the overall impedance.
- Insulation Thickness: Thicker insulation between windings can increase leakage reactance.
In summary, the percentage impedance is a fundamental characteristic of a transformer that provides valuable insights into its performance under various operating conditions, especially during fault situations and when paralleling with other transformers.
Mathematical Problems Solved:
- A transformer of rating 132000/6600 volts transformer has a measured impedance drop of 600 volts. What is the percentage impedance of the transformer?
Solution:
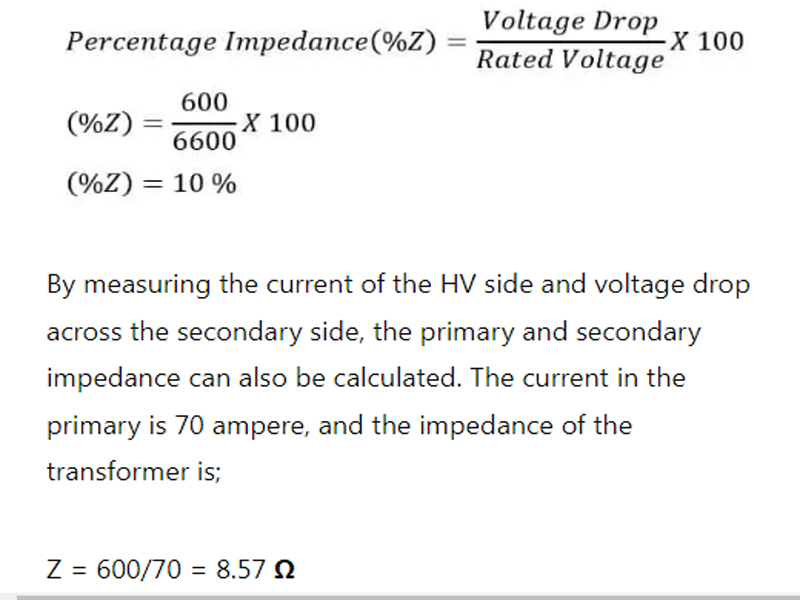
2. Calculating Impedance Voltage
Given:
- A 100 kVA, 11 kV/415 V transformer
- Full-load current on the HV side = ?
- Voltage required to circulate full-load current during short-circuit test = 550 V
Find: Percentage impedance
Solution:
Given:
- Transformer rating: 100 kVA
- Primary (HV) voltage: 11,000 V
- Secondary (LV) voltage: 415 V
- Voltage required to circulate full-load current during short-circuit test: 550 V
- This short-circuit voltage is measured on the HV side (since full-load current is being circulated from the HV side)
Solution:
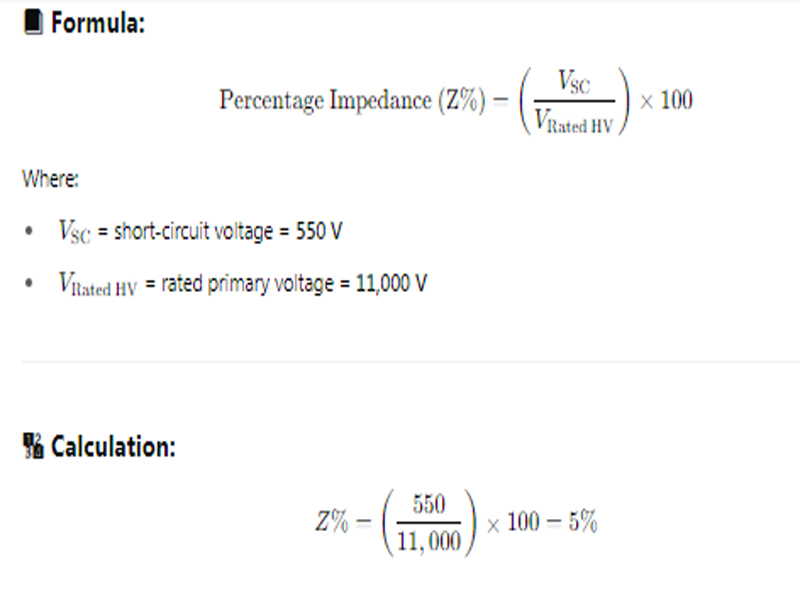
The percentage impedance of the transformer is 5%.
- A 250 kVA, 11 kV / 400 V, 3-phase transformer has a percentage impedance of 4.5%. What voltage needs to be applied to the HV side during a short-circuit test to circulate full-load current?
Solution:

495 volts must be applied to the HV side to circulate full-load current during the short-circuit test.
- A 500 kVA transformer has a percentage impedance of 6%. Calculate the full-load impedance of the transformer in ohms (referred to the HV side, if the HV voltage is 33 kV).
Solution :
Given:

The full-load impedance of the transformer (referred to the HV side) is .
- Two transformers, A and B, are connected in parallel. Transformer A is 500 kVA with 5% impedance. Transformer B is 750 kVA with 5% impedance. If they supply a total load of 1000 kVA, how much load does each transformer supply?
Solution:
Given:
- Transformer A:
- Rating SA=500 kVA
- Percentage impedance ZA%=5%
- Transformer B:
- Rating SB=750 kVA
- Percentage impedance ZB%=5%
- Total load supplied by both transformers: Stotal = 1000kVA
Since both transformers have the same percentage impedance (5%), we need to convert the impedances referred to a common base to calculate the current or load division.

Transformer A supplies and Transformer B supplies .
- A 75 kVA, single-phase transformer has an impedance of 0.045 pu (per unit). Convert this per unit impedance to percentage impedance.
Solution:

The percentage impedance is .
- A transformer has a rated primary voltage of 13.2 kV and a percentage impedance of 5.5%. During a short-circuit test, the full-load current on the primary side is 20 A. What is the impedance of the transformer in ohms (referred to the primary side)?
Solution:

The impedance of the transformer (referred to the primary side) is .