3-Phase Induction Motor
A 3-phase induction motor is an electric motor powered by a three-phase power supply. It converts three-phase electrical power into mechanical power through electromagnetic induction.
It consists of a stator (stationary part) with windings that create a rotating magnetic field and a rotor (rotating part) that is induced to rotate by this field. It is one of the most commonly used electric motors in industrial and commercial applications due to its simple design, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Types of 3-Phase Induction Motors
The primary classification is based on the rotor design:
Squirrel Cage Induction Motor:
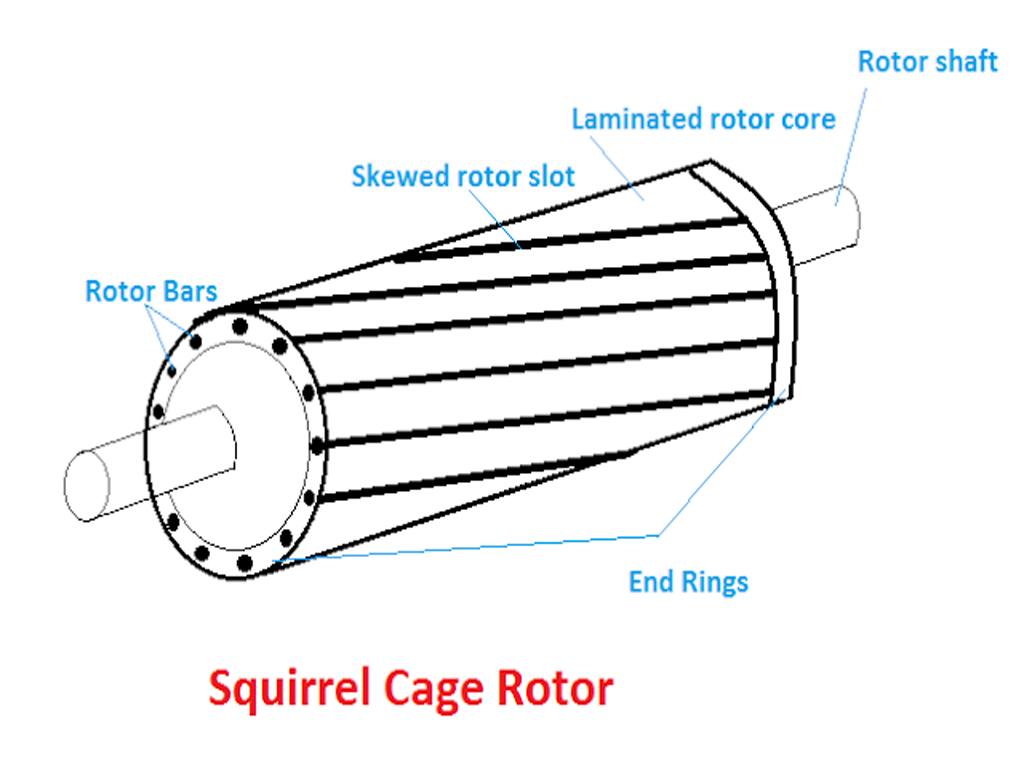
- The rotor consists of laminated iron cores with aluminum or copper bars placed on the surface.
- The rotor has no external connections, and the bars are short-circuited at the ends, forming a closed loop.
- It’s simple, robust, and cost-effective.
- Primarily used for applications requiring constant speed.
Slip-Ring (Wound Rotor) Induction Motor:
- The rotor has windings connected to slip rings.
- External resistance can be connected to the rotor windings via slip rings for controlling motor speed or torque.
- Used for applications requiring high starting torque or variable speed, such as cranes and hoists.
Construction:
A 3-phase induction motor consists of the following main parts:
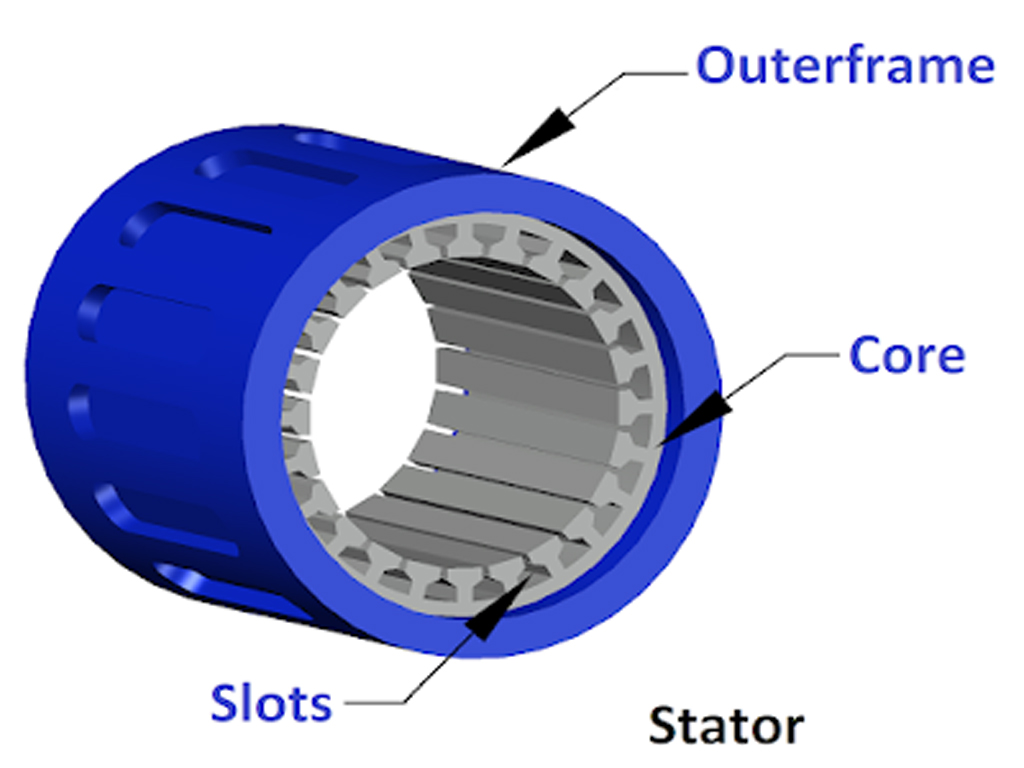
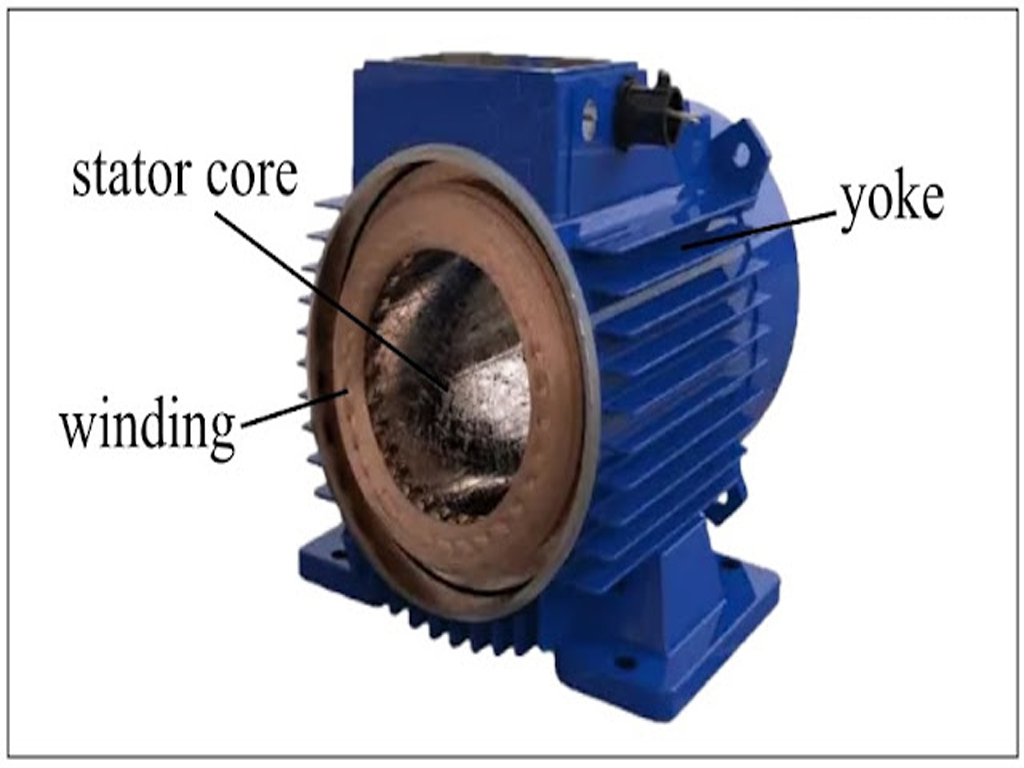
- Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of laminated steel sheets to reduce eddy current losses. The stator has three-phase winding placed in the slots, which are connected to a 3-phase power supply.It produces a rotating magnetic field when the 3-phase current passes through the windings.
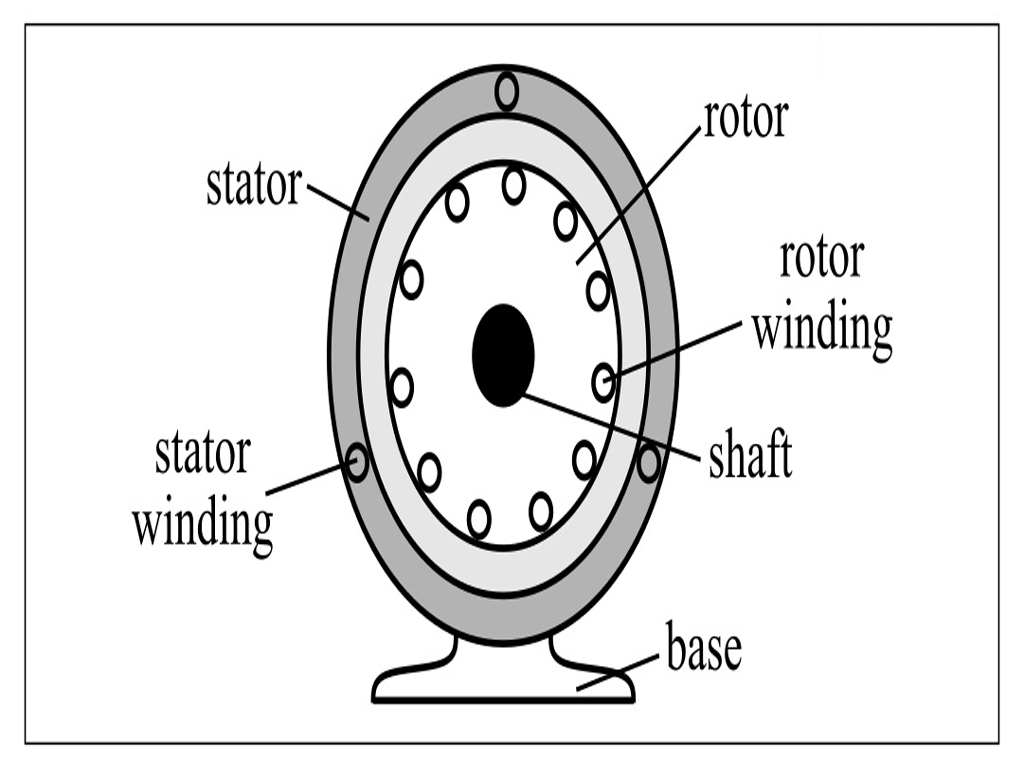
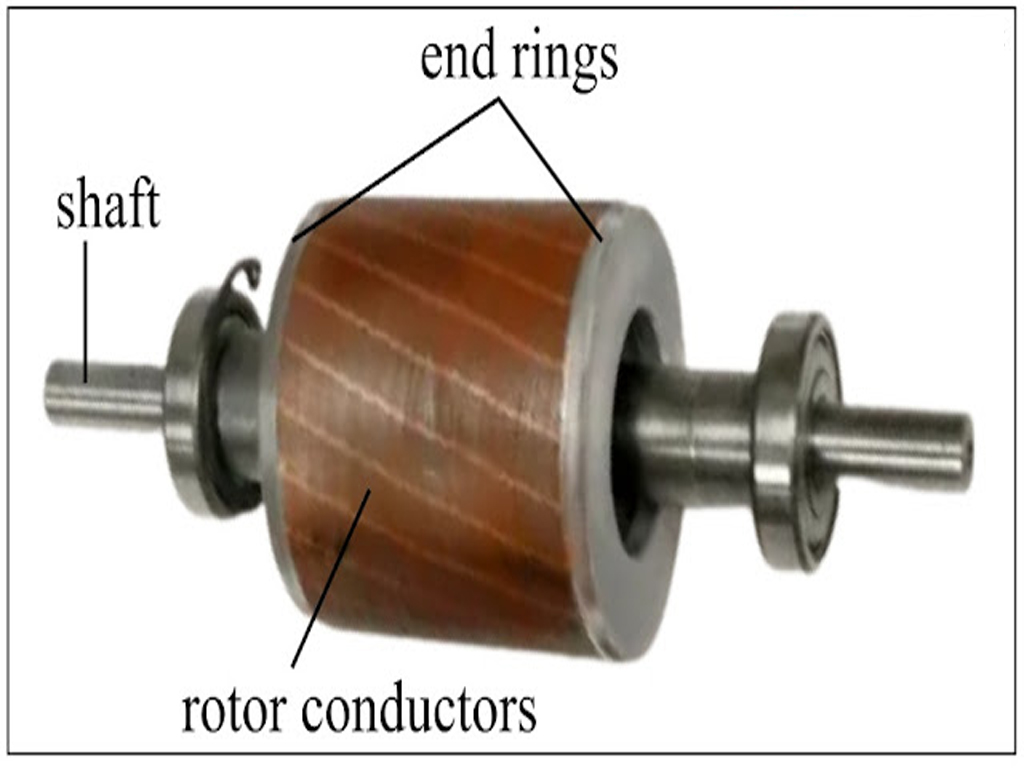
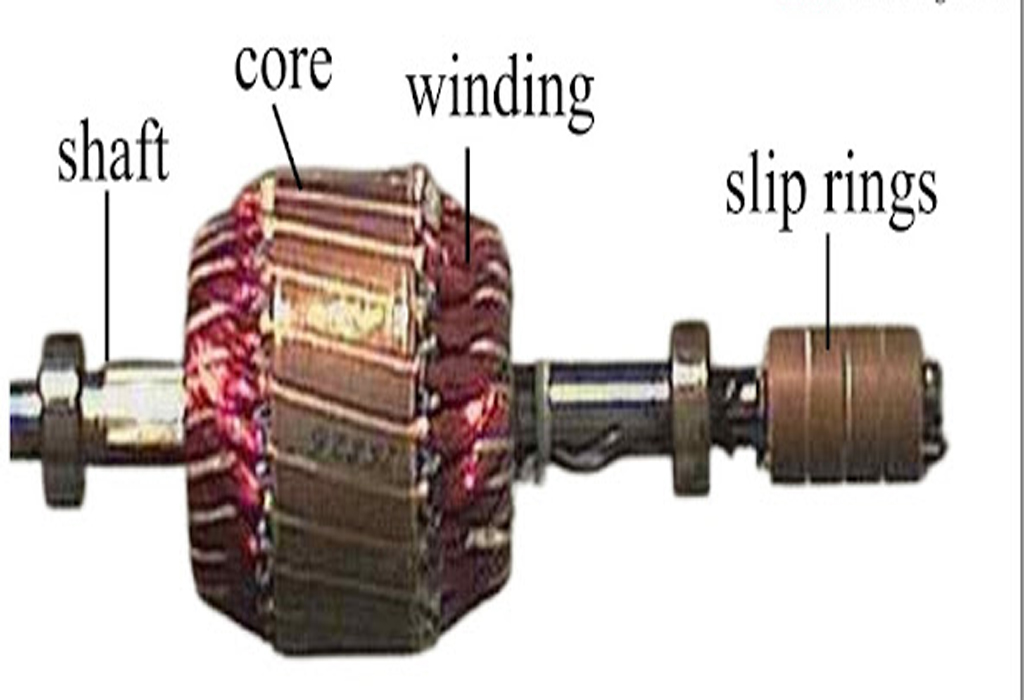
- Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, and there are two main types:
- Squirrel-cage Rotor: This type is the most common. It consists of laminated steel sheets, with conducting bars (usually made of copper or aluminum) short-circuited at both ends by end rings.
- Wound Rotor: This rotor has a three-phase winding, similar to the stator winding, and is connected to external resistors or a controller.
- Shaft: The shaft connects to the rotor and is responsible for transferring mechanical power to the load.
- Bearings: Bearings are used to support the rotor and allow it to rotate smoothly.
Working Principle of 3-Phase Induction Motor:
The working principle of a 3-phase induction motor is based on electromagnetic induction. Here’s how it works:
- Rotating Magnetic Field: When a 3-phase alternating current (AC) supply is provided to the stator windings, it generates a rotating magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field rotates at a synchronous speed, which depends on the supply frequency and the number of poles in the motor.
- Induced Current in the Rotor: As the rotating magnetic field passes through the rotor, it induces a current in the rotor conductors due to electromagnetic induction (as per Faraday’s law of induction). This induced current creates a magnetic field that interacts with the stator’s rotating magnetic field, causing the rotor to rotate.
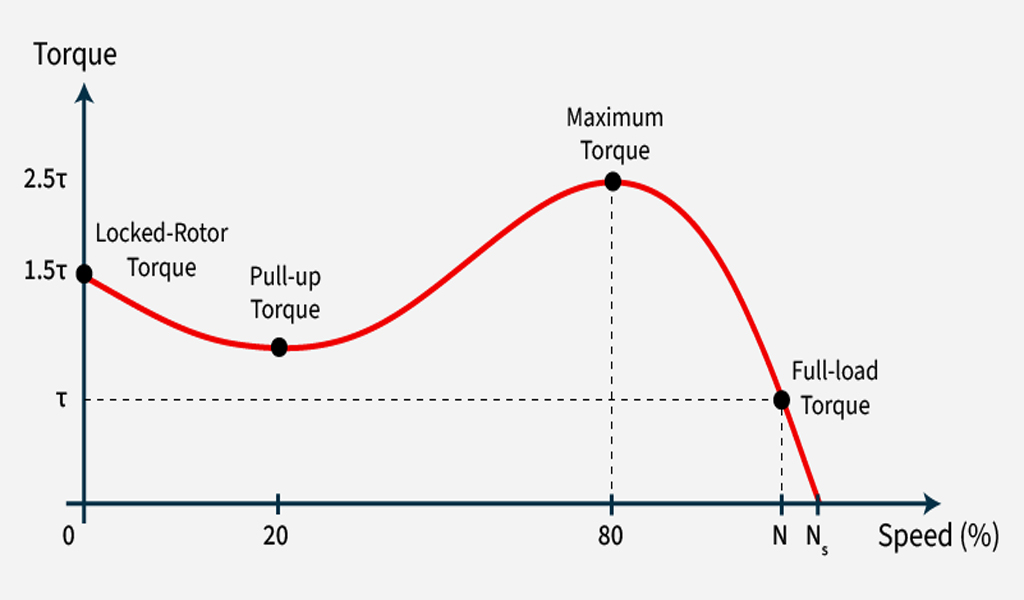
- Slip: The rotor always tries to catch up with the rotating magnetic field of the stator, but it never does, resulting in a phenomenon called slip.
The slip is the difference between the synchronous speed of the rotating magnetic field and the actual speed of the rotor.
The rotor speed can never reach the synchronous speed, as this would imply no relative motion between the magnetic field and the rotor, and therefore no induced current.
Advantages of 3-Phase Induction Motor:
- Simplicity: These motors are simple in construction and design, requiring less maintenance compared to other types of motors.
- Reliability: 3-phase induction motors are very reliable and durable, with fewer chances of failure since they have fewer parts (especially compared to DC motors).
- Self-starting: Induction motors do not need any external starting devices as they are self-starting. The rotating magnetic field generated by the stator is sufficient to start the motor.
- Efficiency: They are highly efficient, especially under load conditions, as they operate on a constant speed.
- Cost-effective: 3-phase motors are cost-effective to produce, and their maintenance cost is relatively low.
- Power Factor: When properly designed and installed, 3-phase induction motors offer good power factor characteristics.
Disadvantages of 3-Phase Induction Motor:
- Low Starting Torque: Induction motors typically have lower starting torque compared to other motors like DC motors or synchronous motors. However, this can be addressed with special designs or external starting mechanisms.
- Speed Control: Speed control is more complicated in 3-phase induction motors, as it generally requires varying the supply voltage or frequency.
- No Speed Regulation: The speed of an induction motor is affected by the load; it is not constant under varying load conditions.
- Slip Losses: Due to the nature of the induction process, there are inherent losses caused by the slip. The more the slip, the greater the loss.
- Higher Power Factor Requirement: To maintain the efficiency of operation, it is often necessary to have power factor correction systems in place, especially when the load is fluctuating or highly inductive.
Industrial Applications:
- Pumps: Used in water supply systems, irrigation, and various industrial fluid transfer processes.
- Fans and Blowers: Essential for ventilation, air conditioning, and industrial exhaust systems.
- Compressors: Powering air compressors for pneumatic tools and industrial processes.
- Conveyors: Driving material handling systems in factories and warehouses.
- Machine Tools: Used in lathes, milling machines, and other metalworking equipment.
- Cranes and Hoists: Providing the lifting power for heavy loads in construction and manufacturing.
- Textile Industry: Driving various machines involved in textile production.
- Mining: Used in crushers, and other heavy equipment.
- Oil and Gas: Used in oil extracting mills, and in pumping applications.
Commercial Applications:
- HVAC Systems: Powering large air conditioning units and ventilation systems in buildings.
- Elevators and Escalators: Providing reliable and efficient vertical transportation.
MCQ Quiz Test Three Phase Induction Motor:
Three Phase Induction Motor part-1
Three Phase Induction Motor part-2
Three Phase Induction Motor part-3
Three Phase Induction Motor part-4
MCQ Quiz Test Single Phase Induction Motor:
Single Phase Induction Motor part-1
Single Phase Induction Motor part-2
Single Phase Induction Motor part-3
Single Phase Induction Motor part-4
Related posts:
Torque In Three Phase Induction Motor
Speed Control Methods Of Three Phase Induction Motor
Losses In Induction Motor
Equivalent Circuit Of Induction Motor
Single Phase Induction Motor